At present, 90% of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is found in older adults, and it is a major health problem in all countries. Blood sugar level is relatively higher and longer when getting older. This results in the deterioration of organs and the failure of systems in the body. Also, complications in older adults with diabetes seem to be more severe than those of younger people with diabetes.1,2 Older adults with T2DM should be examined annually for complications and instructed how to use practices to control blood sugar level, blood pressure and blood lipid. The American Diabetes Association3 and The International Diabetes Federation4 suggest that the HbA1c level of older adults should be between 7% - 8% in order to maintain their ability to function properly or to have quality of life.
Diabetic foot is a complication that causes amputation in patients with diabetes around the world, affecting approximately 70% of patients, that’s one every 30 seconds. The diabetic patients with diabetic foot ulcers lose a leg or a foot at the rate of 13.7 person/one thousand/year, which is 25 times higher than those who do not have diabetes. The mortality rate in the last five years was also higher than those without a history of diabetic foot ulcers.5 The important cause of foot complications is peripheral arterial disease. It is found in about 10-60% of cases associated with peripheral neuropathy and/or infection6 which is often found in people with diabetes who cannot control blood glucose levels and have diabetes for more than 10 years.7 It occurs because of a complex reaction of the fat pads accumulation process due to hyperglycemia with insulin resistance and the retention of sorbitol and fructose in the walls of blood vessels which clogs small blood vessels. As a result, the peripheral vascular circulation decreases and it results in nerve-axon reflex. There is also congestion of neurons which causes nerve degeneration. Tiny blood vessels that moisten the wall of the aorta also malfunction causing the loss of elasticity of blood vessels, which causes atherosclerosis.8 Inaddition, the function of the inner lining of the arteries decreases and the secretion of nitric oxide, which is a substance that is able to dilate the blood vessels and control the operation of all vessels, also decreases.9,10 It also restrains the immune system and prevents atherosclerosis. When the secretion of nitric oxide decreases, the blood vessels become gradually narrower, making blood sugar levels rise. The cells of vascular smooth muscle are inflammatory making the coronary narrower which eventually causes peripheral arterial disease.11
The evaluation of ABI in order to assess the peripheral arterial disease is commonly done by measuring the pressure of the peripheral arteries. It is the analysis of the ratio of systolic pressure of the ankle atdorsalispedis and posteriatibial. The highest value is divided by the highest value of systolic pressure of the arm. The ABI is measured by using the doppler ultrasound with wrist blood pressure monitor. The average value ranges from 0.91 to 1.30; the mild to moderate level ranges from 0.41 to 0.90 and the severe level ranges from 0.00 to 0.40.12 Those with value < 0.8 often have leg pain while walking with weak pulse of the foot or ankle. If the value < 0.40, patients receives treatment for ischemic rest pain, ischemic ulcers or necrosis and the pulses at foot and ankle cannot be palpated.13
The chronic non-communicable diseases report of the year 2014 of Manorom Hospital, Chai Nat Province found that there were 876 older adults with T2DM (59.71%) of the people with T2DM aged 15 years old and over. HbA1c level of 485 (55.34%) older adults was higher than 7%. Also 283 (58.35%) of them had HbA1c higher than 8%. The screening for foot complications in 851(97.15%) older adults with T2DM showed that 392 (46.06%) of them had the risk of diabetic foot ulcers in the moderate to high level, and 16 (1.09%) of them lost feet or legs by amputation. Moreover, 176 (20.68%) of them had mild to moderate ABI. The researchers also found that the older adults with T2DM who cannot control HbA1c level their risk of having diabetic foot ulcers did not decrease and this can result in the incidence of losing feet and legs by amputation. Therefore, seeking knowledge and approaches from other alternative treatments is recommended.
The researchers realized the importance of foot reflexology as the integration of philosophy of oriental medicine and western medicine which is the combined approach for health care that has been continuously used from the past to present. It is based on Zone theory and Meridian theory. It is both science and art based on scientific principles, which describes the effects of foot reflexology to all the organs, glands and body parts.
For example, toes represent head, and foot represents chest, heart and lungs. Two hands and a wooden stick are used to massage or press to these points to balance the functioning of various organs in the body which stimulate the energy flowing in the body, resulting in effective nervous system, muscular system, endocrine, lymphatic system, improved blood circulation and the body’s immune system to function effectively and restore balance.14 This promotes holistic care of the physical, mental, social and spiritual dimensions which affect diabetes as the synthesis of glucose into the cells decreases, resulting in lower blood sugar levels. It also decreases the complications of diabetes, so the people with diabetes are healthier. This is consistent with the study of Jeong15 which studied the effects of self-foot reflexology in patients with T2DM and found that it helped reduce peripheral neuropathy, especially numbness and pain and stimulated the circulation of blood to the feet directly which helped reduce the loss of sensation to the foot and the foot pressure.16 It also decreased HbA1c two hours after a meal and reduced pain and numbness of the feet which was the result of peripheral nervous system complications in people with diabetes.17 Castro-Sánchez, et al.18 also found that the blood pressure of the lower legs and the blood circulation in the leg increased significantly.The statistics showed that massage for relaxation allowed better circulation of the blood vessels in the legs of the people with T2DM. If foot reflexology, which is a method that requires dexterity and precision and provides more specific benefits, was used, it would help slow down the severity of the peripheral vascular disease in the people with T2DM and effectively reduce the loss of feet or legs.
This research is a randomized experimental design with a randomized controlled two-group pretest-posttest design. The purpose of the study was to investigate the effects of foot reflexology integrated with medication use on HbA1c and ABI in older adults with T2DM who sought treatment at the diabetes clinic of Manorom Hospital, Manorom District, Chai Nat Province between January 5, 2015 and June 30, 2015. The study sample consisted of 40 older adults with T2DM who met the inclusion criteria:
The samples were recruited from those who had received treatment at the diabetes clinic and were qualified according to the criteria set. The probability sampling method was employed in the study. The samples were randomly selected from the sampling frame and the systematic sampling by computer was employed to select the samples into the experimental group. All samples were proportionally allocated according to the numbers of samples found each day. After that, the samples were slected by simple random sampling by means of drawing lots. Fifty lots were prepared according to the numbers of the samples. The samples were divided into a control group and an experimental group, so the lots were written with number 1 and number 2. Number 1 was for an experi-mental group while number 2 was for a control group. The samples drew a lot themselves. Similar age and duration of having diabetes were considered in order to have the similarities of the samples. Two to eight samples per day were willing to participate in the study.
The sample size determination: in this study, G*Power 3.0.10 program was employed. The sample size was deter- mined according to the principles of Power analysis. The effect size was 1.04. The power of test was set at 0.95. The significance level was 0.05. The sample size was 20 people for each group. They were randomly assigned to the experimental group and the control group
The instruments used in this study can be divided into two categories:
1.Data collection instruments:
a. The personal information record and
b. The foot screening forms
2.Research instruments:
a. Handheld doppler probe, Ultratech Brand, PD1ev Model which provided the accuracy of 87%.It was the physical measurement for the diagnosis of peripheral artery disease.
b. ARRAY HighPerformanceLiquid Chromatography (HPLC) by Immune – turbidity, which passed the standards of the manufacturer, and was checked for accuracy before being used every day.
c. Manuals and instructions of foot reflexology demonstrating the steps of foot reflexology which were taken from the video teaching about foot reflexology.19
d. Massage tools, including wooden sticks for foot reflexology, lotion balm, two towels and an adjustable couch
The researchers attended the 32 hours foot reflexology workshop organized by Assistant Professor Dr. Ladaval Ounprasertpong Nicharojana who is an expert in foot reflexology. The researchers had been trained for 1 month and achieved proficiency. The massage used in the study was using two hands to squeeze, press, roll, rub and stimulate muscles at feet, calves, knees and foldable joints of both legs and reflexology was performed at each point of the feet, which represents 62 organs to balance energy. A wooden stick was used to press down on 26 points to boost up energy, and a wooden stick was used to press on 13 points associated with the reduction of blood sugar levels; 15 minutes for each foot, including 30 minutes according to the instructions.
The older adults with T2DM who received services at the diabetes clinic, outpatient department of Manorom Hospital received foot reflexology according to the schedule by the researchers every day; 30 minutes a day. Not more than 6 samples/day received foot reflexology. The control group did not receive foot reflexology.
The researchers also gave advice on diet, exercise or medical use to the control group, which did not differ from the experimental group and they received massage after the results of the study were gained according to the hypothesis of the study. When the two months foot reflexology program ended, HbA1c and ABI of the experimental group were measured immediately.
The data collection was conducted after receiving approval from the Human Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medical, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University (Approval No. 2014/566), and approval from the Medical Director at Manorom Hospital, ChaiNat Province. The samples were willing and signed a consent form to participate in the study.
The statistical analysis was as follows:
- Part 1: General information; gender, age, religion, marital status, educational level, occupation, average salary, the right of treatment, the duration of having diabetes, other congenital diseases, smoking history and exercise were analyzed using frequency and foot assessment was analyzed using descriptive statistics.
- Part 2: HbA1c and ABI before and after receiving massage for 2 months were compared. The percentage,mean, standard deviation and difference between the mean of 2 groups were analyzed by Independent t-test and Paired t-test.
The study sample consisted of 40 older adults with T2DM who sought treatment at the diabetes clinic who met the inclusion criteria. The subjects were recruited through random sampling, with 20 assigned into the experimental group and the other 20 into the control group.There were more female than male (75%) with an average age of 65.25±4.61 years, the control groupan average age of 64.45±4.19 years, andthe experimental group an average age of 66.05+4.98 years. The average duration of having diabetes was 13.98 years. The aveage duration of having diabetes in the control group was 14.25 years, and that of the experimental group was 13.70 years. They also had chronic diseases and other compli- cations (92.5%), most of which were diabetic in nature, such as neuropathy (72.5%), followed by hypertension (70.0%) and hyperlipidemia (52.5%). They were treated with 2 types of oral hypoglycemic agents (87.5%) and the majority did not do exercise (92.5%) (Table 1).
The average levels of HbA1c and ABI of the older adults with T2DM of the group which received 2 months foot reflexology program and the group which did not receive the foot reflexology were compared. However, since the basic data of the two groups were different, the differences of the average value of the peripheral artery were compared instead in order to test the hypothesis of the study. It was found that after receiving the foot reflexology program for 2 months, the average HbA1c level of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group, and statistically significant at 0.05 level (t = 2.76, p = 0.009, SD = 1.37), and the average value of the peripheral artery was higher than that of the control group,and statistically significant at 0.001 level (t = 5.921, p <0.001, SD = 0.044 and t = 9.155, p = < 0.001, SD = 0.016,respectively) (Table 2-5).
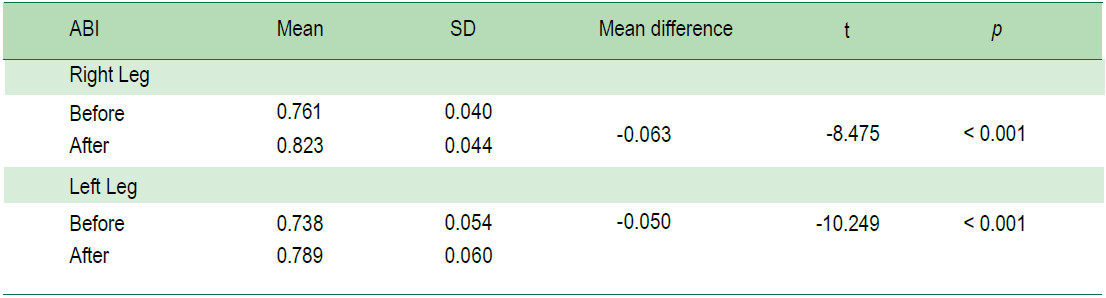
The comparison of the average levels of HbA1c and ABI of the older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus of the control group after receiving the foot reflexology program for 2 months showed that the average HbA1c level was lower than before receiving the foot reflexology program, and statistically significant at 0.001 level (t = 10.54, p < 0.001, SD = 0.96) and the ABI was higher than that of be- fore receiving the program, and statistically significant at .001 level (t = -8.475, p < 0.001, SD = 0.044 and t = -10.249, p < 0.001, SD = 0.060, respectively) (Table 6-7).
Table 1: The number and percentage of the control group and the experimental group categorized by the background and diabetes information (n=40).
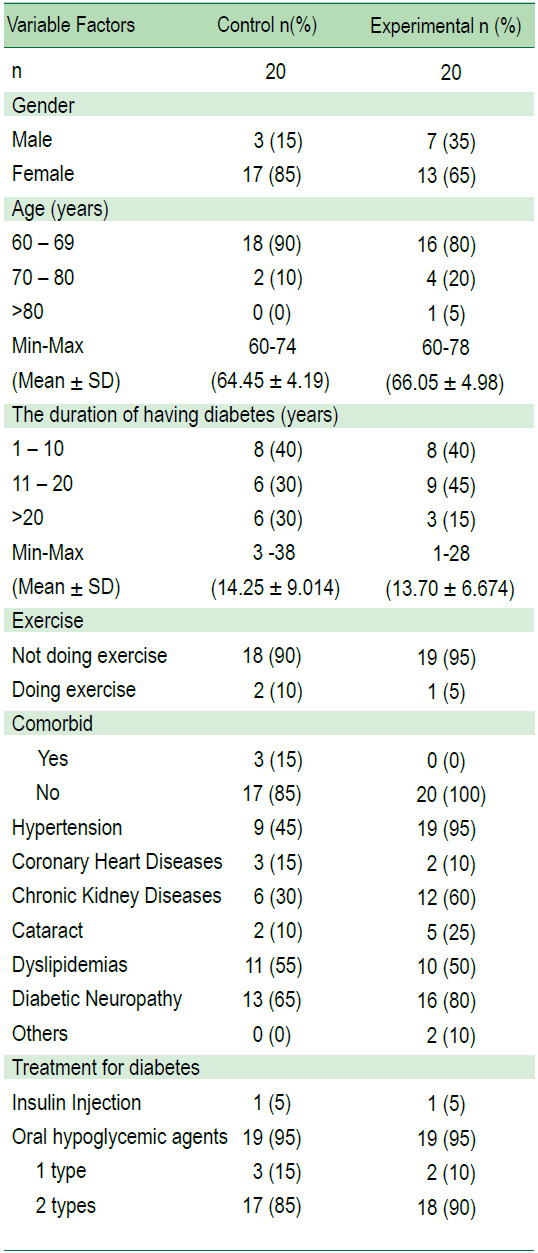
Table 2: Compare HbA1c levels between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
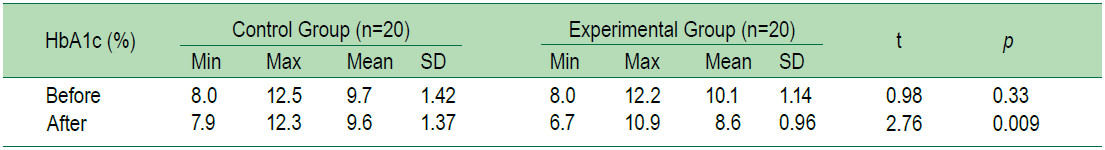 Table 3: Compare ABI-Right leg between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
Table 3: Compare ABI-Right leg between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
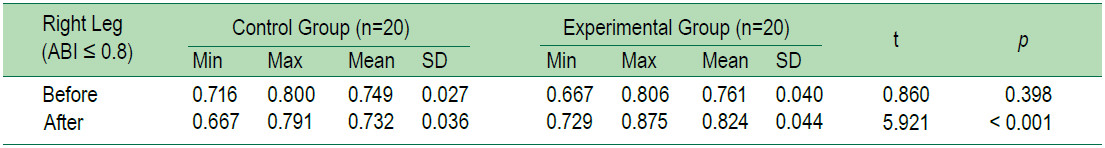 Table 4: Compare ABI-Left leg between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
Table 4: Compare ABI-Left leg between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
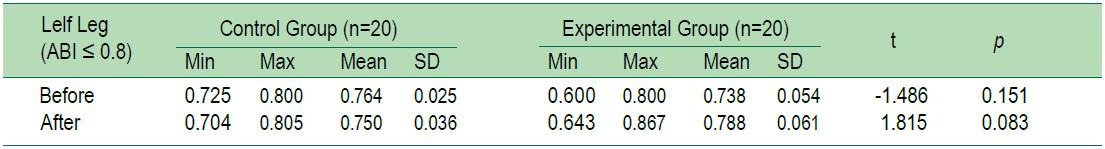 Table 5: Compare Mean difference ABI between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
Table 5: Compare Mean difference ABI between the experimental group and the control group two months after receiving the foot reflexology program.
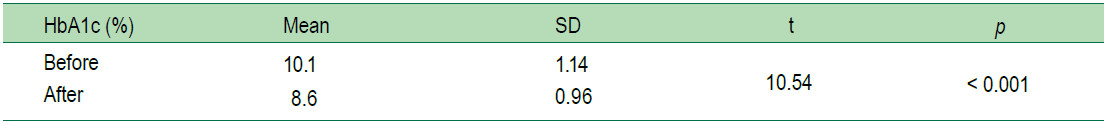 Table 6: Compare HbA1c in the experimental group before and two months after receiving the foot reflexology program (n = 20).
Table 6: Compare HbA1c in the experimental group before and two months after receiving the foot reflexology program (n = 20).
 Table 7: Compare ABI in the experimental group before and two months after receiving the foot reflexology program (n = 20).
Table 7: Compare ABI in the experimental group before and two months after receiving the foot reflexology program (n = 20).
The results of this study revealed that foot reflexology integrated with western medical practices helped reduce HbA1c and increase ABI, and both were statistically significant. The explanation is that foot reflexology when integrated with western medical practices had effects on HbA1c and ABI since foot reflexology is to squeeze, press, roll, rub and stimulate foot muscles, calves, knees and foldable joints of both legs. Reflexology also employs a wooden stick to massage on points on foot, bringing the cardiovascular system, endocrine glands, lymph nodes and respiratory system back into balance. The invisible energy can flow smoothly and is relative to the control mechanism of HbA1c and ABI, including the synthesis of glucose of the livers and the pancreas to balance insulin secretion and to allow insulin to work more efficiently in importing sugar into the cells.20, 21 Also, when HbA1c level drops, foot reflexology will send energy through the mechanisms of the autonomic nervous system, kidneys system and circulatory system. So, arteries can be more flexible. Nitric oxide also increases, which promotes vasodilation and helps the flow of blood to feet. As a result,blood pressure at the legs increases causing an increase of ABI.22 This is consistent with the study of Sakdanu- parp23 who studied the effects of foot reflexology on blood glucose levels and numbness of the patients with T2DM and found that the HbA1c level decreased. In addition, the current study also found that the average value of ABI of the control group which did not receive foot reflexology decreased, which may result in more severe peripheral arterial disease.
Foot reflexology can help reduce HbA1c and increase ABI in older adults with T2DM. It can be implemented as a complementary therapy to control diabetes and reduce severity of complications in diabetic foot in older adults with T2DM.
I would like to thank the Medical Director, Head of Nursing, and all staff at Manorom Hospital for their help and contributions in making this research a success.