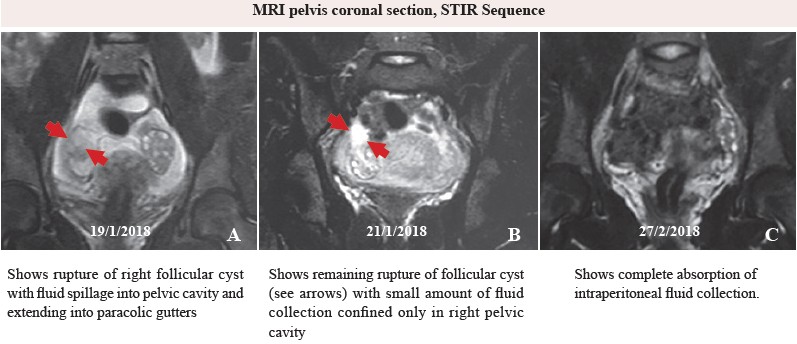
A 27-year-old unmarried woman with acute intermittent abdominal pain for 6 hours without nausea, vomiting or fever.Urination and defecation were also normal. No leucorrhea was found in this patient. Pelvic examination appeared tobe normal. Others physical examination revealed tenderness with mild guarding at right lower abdomen. Laboratoryfindings: hemoglobin 10.8 g/dL, white blood cell 11.73 103/μL , Neutrophil 80.1%, Lymphocyte 14.4%, Monocyte 3.1%,Eosinophil 1.0%, and platelet was in normal range. Provisional diagnosis was acute appendicitis versus rupture of ovarian cyst.Pelvic Ultrasonogram was chosen to be primary imaging revealing moderate amount of fluid in pelvic cavity and extended toboth lumbar gutters and the appendix was not identified. Consequently, MRI pelvis was performed instead, the findings showedrupture of right ovarian cyst (see Fig. A). Management was conservative treatment and follow up with MRI imaging untilcomplete absorption of fluid in pelvic cavity. (Fig. B-C).
Rupture of an ovarian cyst may occur in physiologic or pathologic conditions. The physiologic condition is rupture offollicular cyst in every ovulatory cycle. It is usually asymptomatic or may cause pain in mid cycle. Raziel A, et al.1 reported 70cases with ruptured corpus luteal cyst, surgical intervention was performed in 58 cases (83%). For this reason MR pelvis mayhelp the physician in case of doubt from clinical symptoms and findings which may avoid surgery. Ruptured serous fluid orblood is the reason for irritation in the peritoneal cavity. Management including observation, analgesics or surgical interventiondepends on severity of symptoms or hemodynamic instability. Nevertheless, some pathologic conditions such as dermoid cyst,ovarian cancers, ectopic pregnancy or adnexal torsion can be the causes of ruptured ovarian cyst presenting symptoms as sameas after a physiologic condition and a pelvic Ultrasonogram is the first investigation in these cases. In this study, we present acase of physiological ovarian cyst rupture by MRI STIR sequence from initial ovarian cyst rupture until complete closure andabsorption of intraperitoneal fluid collection. Interval MR Study can confirm the diagnosis.